Following the effects of the past
How did South Africa deal with its economic challenges?
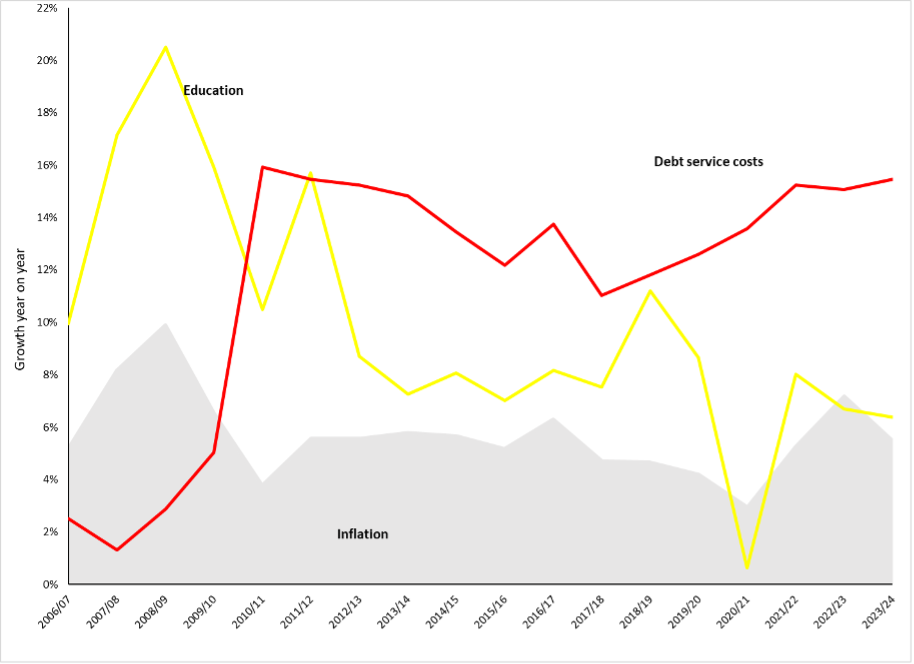
- In 1994, South Africa inherited a debt crisis, but policies reduced debt from 44% to less than 20% of GDP.
- Government focused on redistribution and growth to increase funding for social sectors like education and health.
- By 2006, the budget was in surplus, but deficits returned after the 2008 global financial crisis.
What impact did corruption have on the economy?
- The State Capture Report revealed widespread corruption that cost South Africa billions.
- Covid-19 worsened the economic situation, leading to higher debt and interest costs.
- Debt-to-GDP ratio increased from 20% in 2008 to 74% by the end of 2023.
What are the challenges facing education in South Africa?
- South Africa allocates over 6% of GDP to education, but issues such as fees and poor infrastructure persist.
- Classroom overcrowding, lack of access for poor learners, and inadequate teacher training impact quality education.
- Debt has limited growth in education spending, affecting resource availability for schools.
In conclusion, South Africa’s economic challenges, compounded by corruption and debt, pose significant obstacles to providing quality education for all. Transformative efforts are needed to address institutional weaknesses, reduce corruption, and prioritize investment in education to secure the country’s future.
Source: www.amnesty.org