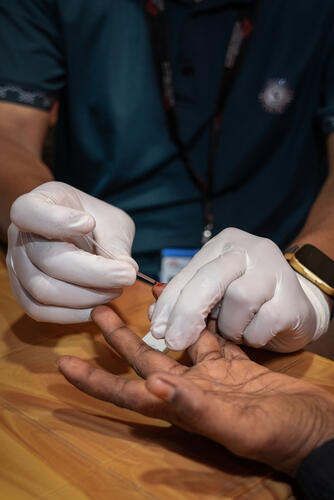
What is the Impact of Hepatitis C Infection among Rohingya Refugees?
A study conducted by Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) reveals that nearly one-fifth of Rohingya refugees in Cox’s Bazar camps in Bangladesh are currently infected with hepatitis C, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Why are Hepatitis C Infections Prevalent in the Refugee Camps?
The lack of access to healthcare and safe medical practices, coupled with the overcrowded living conditions, has contributed to the high prevalence of hepatitis C among the Rohingya population in the camps.
What Challenges Do Hepatitis C Patients Face in the Camps?
- Limited access to diagnosis and treatment
- Inability to afford expensive tests and medication
- Dependence on alternative methods of care
What Measures Are Being Taken to Address the Hepatitis C Crisis?
MSF is advocating for a joint humanitarian effort to combat the disease and has been the primary provider of hepatitis C care in the camps for four years. However, a large-scale prevention campaign is needed to limit transmission and provide adequate treatment.
How Is the Treatment of Hepatitis C Being Prioritized in the Camps?
MSF has treated over 8,000 patients with confirmed active infections in Cox’s Bazar camps since October 2020, highlighting the urgent need for expanded treatment capacity and affordable diagnostic tests.
Ultimately, the battle against hepatitis C among Rohingya refugees in Cox’s Bazar calls for a collaborative effort to provide accessible and affordable healthcare, promoting the well-being of this vulnerable population.
Source: www.msf.org